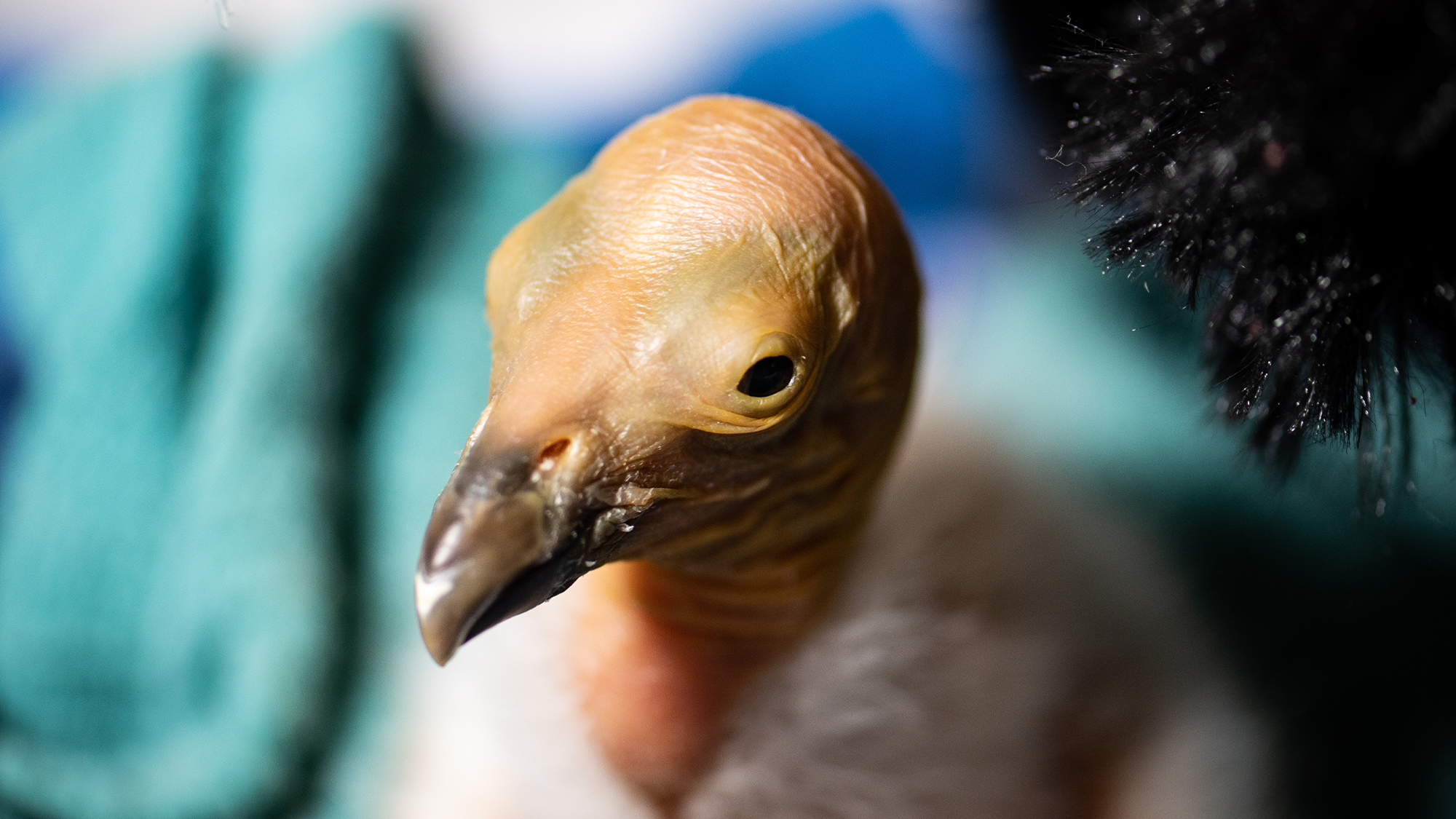


On May 9, a baby California condor hatched at Liberty Wildlife, a wildlife rehabilitation, education, and conservation organization in Phoenix, Arizona. The hatching is a ray of hope and welcome good news for the struggling species that was only recently brought back from the brink of extinction.
Only 22 condors were believed to be alive during the 1980s after a maelstrom of habitat loss, poaching, lead poisoning accidents with power lines, and the insecticide DDT. Currently, about 275 wild birds are cruising the skies about California, Utah, Arizona, and Baja California, Mexico, more than 160 are in captivity, and more than 400 live worldwide.
[Related: Inside the Yurok Tribe’s mission to make critically endangered condors thrive.]
The largest bird species in North America and a crucial part of the ecosystem, California condors are considered sacred to many indigenous peoples. The Yurok Tribe of the Pacific Northwest call California condors “prey-go-neesh,” and say the birds have been tied to the Yurok Hlkelonah, or the cultural and ecological landscape, since the beginning of time. The tribe has officially been a driving force on condor reintroduction since 2008.
Now, these sacred and important birds face a grave threat in the form of a tiny pathogen. Highly pathogenic avian influenza (H5N1), also called bird flu, is threatening condors at an alarming rate. It was first detected in the California condor in late March, and more than 20 are known to have died since.
“It is scary particularly for endangered species like the California condors. It has the ability to wipe out an entire species,” Liberty Wildlife’s Animal Care Coordinator Jan Miller tells PopSci.
One of the birds that succumbed to the disease was the new hatchling’s mother, part of a breeding pair of wild California condors. The mother was found acting suspicious in a cave near the Grand Canyon and was brought to Liberty Wildlife due to suspected bird flu. She died eight days later.
“Using telemetry, it was assumed that she had laid an egg, probably between March 13 and March 17, and it was predicted to hatch between May 9 and May 17,” Liberty Wildlife’s Executive Director Megan Mosby tells PopSci. “The limited movement of the male led to the assumption that he was trying to incubate an egg. The biologists at the Arizona Vermilion Cliff site decided that it wasn’t safe for the male, a known breeder, to attempt to raise a chick solo and feed himself, especially in a dank, cool cave … a perfect place for flu contamination.”
[Related: Spy tech and rigged eggs help scientists study the secret lives of animals.]
Biologists brought the egg back to Liberty Wildlife, where it was monitored in a structure called a brooder. When the egg began to “pip,” the Los Angeles Zoo’s propagation team advised Liberty Wildlife on best practices for monitoring the hatchling’s progress. The team noticed that the chick was in the wrong position in the egg due to where it had pipped, or poked through its membrane, and that it would need assistance in order for the hatch to be successful.
“Veterinarian Dr. Stephanie Lamb assisted in the freeing of the baby from the egg and the operation was successful. After a health check, a swab to test for Avian Flu was obtained, and the chick was placed in an incubator with a surrogate (stuffed animal) ‘mother’ condor,” Miller says.
The hatchling was negative for bird flu and continued to eat solid food and bond with her surrogate plush parent. According to Mosby, the team was excited to find out she was female because 11 of the 21 condors that have died due to bird flu were breeding age females.
On May 17, she was flown to The Peregrine Fund in Boise, Idaho. There she will be raised by foster parents so that she can one day be released back into Arizona’s skies.
“At this age it is very easy for the chick to imprint on humans so getting her with her own species is critical to her releasability,” says Miller. “The Peregrine Fund has a very advanced propagation department with proven foster parents to help raise chicks for release into the wild. It is a very large operation with proven results.”

According to the team, vultures like the California condor are not only intelligent, but are incredibly necessary to help clean up the environment since they handle dead and decaying animals that can spread disease.
“Vultures are part of the natural cleanup crew in nature. They deserve every fair chance they can get to continue to survive and be a part of this world,” says Miller.
In addition to this welcome hatchling’s continued success this week, the United States Department of Agriculture’s Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service approved the emergency use of bird flu vaccine on May 16. The Yurok Tribe called this move, “a huge step in the effort to combat this virulent threat, but still a long road ahead.”