
Battery life is important to all of us. No matter how powerful, ultra-versatile, and extra-speedy our smartphones are, they’re of no use at all without juice in them.
Android, like iOS, features a low battery mode that kicks in when your gadget’s life expectancy is running low. It’s called Battery Saver and it optimizes power by putting certain performance restrictions, like how often email apps can check for new messages.
But unlike iOS, Android lets you tweak which apps are affected by Battery Saver, so if you absolutely need a particular platform to remain fully operational (albeit at a cost to battery life) you have the option to pick and choose.
How Battery Saver works
Android’s Battery Saver mode limits apps and features so that the system only refreshes content when you open up the relevant app. Also while in this mode, location services will only work while the screen is on, the dark theme will take over, and if you have it enabled, your device will stop continued listening for the “hey Google” command.
Battery Saver mode doesn’t allow apps to run in the background either, and some of your notifications may be delayed. Exactly how this plays out varies from app to app, depending in part on what developers have done with their code. Fitness tracking apps are a good example—they typically run in the background syncing your stats as you go, but since they’re not essential to the functioning of your phone, they’re one of the first tools the system will halt.
[Related: 4 ways to keep your Android phone from dying when you need it most]
Google’s operating system also has an Extreme Battery Saver mode. Honoring its name, this feature goes beyond Battery Saving mode, pausing most apps (effectively disabling their notifications) and slowing down the speed of your phone’s chipset. When in this mode, your device will set your screen’s timeout at 30 seconds, turn off hotspot tethering, and stop the Wi-Fi and Bluetooth radios from scanning for location data
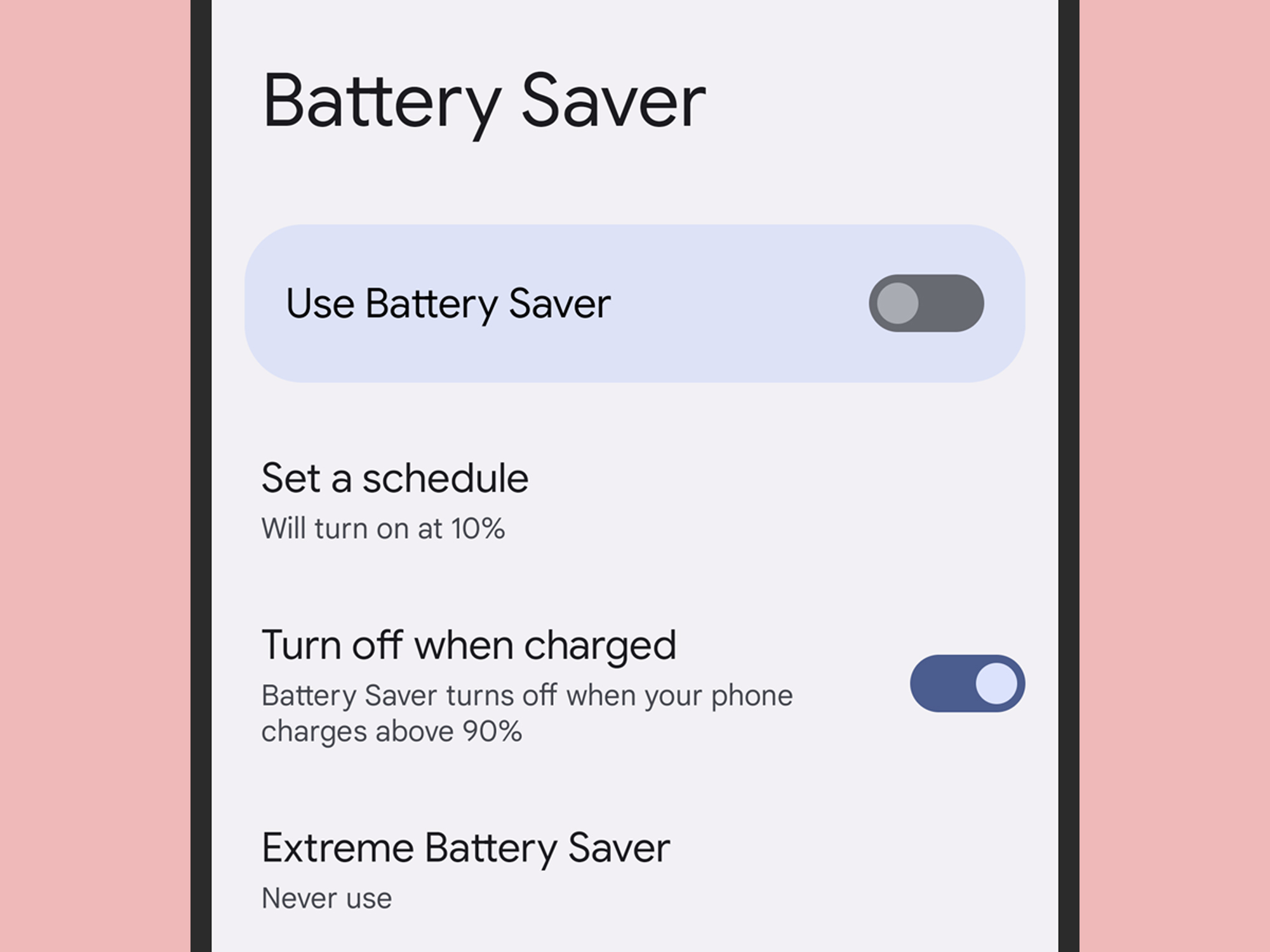
To turn on Battery Saving mode manually, from Settings, head to Battery, pick Battery Saver and toggle the Use Battery Saver switch. To have it turn on automatically, choose Set a schedule—you can use it as part of a typical routine (so Android can make decisions based on when you usually charge your phone), or have it kick in when your device reaches a certain battery percentage.
For an even more thorough power-saving strategy, from the Battery screen, tap Extreme Battery Saver and When to use. You can set it so that whenever Battery Saver turns on you’ll have your phone prompt you to use the extreme mode or activate it automatically. You can also make it so that your device never turns the extreme mode on.
Those instructions apply to Google Pixel phones and other Android handsets with a stock or near-stock version of the operating system. If you’re on an Android device from another manufacturer, these screens may vary slightly. From the Settings app on Samsung phones, for example, tap Battery and device care and then Battery to manage low battery mode.
Setting app exemptions
Now that you know how Battery Saver works, you can start setting exemptions for the apps you want to bypass restrictions—these apps will not slow down, won’t delay notifications, and will be able to run in the background.
But before you start whitelisting apps, keep in mind that it’s difficult to predict precisely how the mode will impact each program, so it might be worth testing out what Battery Saver does at an individual level. Remember that the apps you allow to run as normal are going to drain more battery than they would otherwise.
From Settings, tap Apps and See all apps, and then pick the one you want to exempt from Battery Saver. Select Battery and you’ll find that it’s set to Optimized—this is the default option and it lets Android decide how it manages the app. To reverse this, choose Unrestricted. You can also pick Restricted for apps that you know are big battery hoggers. This essentially keeps Battery Saver activated for that particular app all the time.
[Related: Make your laptop battery last all day]
When Extreme Battery Saver kicks in, the situation changes again. To make apps exempt from this mode, you need to tap Battery from Settings, and then choose Battery Saver, Extreme Battery Saver, and Essential apps. All the critical apps like Clock and Camera are already set to keep running as normal, but you can add apps to this list using the checkboxes next to them.
Again, you might find the menus and options look slightly different if you’re using a phone that isn’t running stock Android. With a Samsung handset, go to Battery and device care and Battery from Settings, tap Background usage limits, and Never sleeping apps. There you’ll be able to pick the programs you don’t want the phone to slow down or pause—tap the + button (top right) to add a new app.
Back on the previous screen, you can tap Power saving to further customize the low battery mode. You can, for example, decide whether the battery saver mode limits the speed of the phone chipset, and whether your device can limit apps in terms of their background activity. These are all options you don’t get with Battery Saver on the standard edition of Android.